Startups thrive on speed. The faster you ship, the sooner you gather user feedback, generate revenue, and outpace competitors. But moving fast comes with trade-offs. Rushed frontend development can lead to technical debt, poor performance, and scalability challenges. The key is balancing speed with long-term stability.
Here’s what startups need to know:
- Framework Choices: Popular options like React make hiring easier but require more setup. Lightweight frameworks like Vue.js or Svelte offer faster development with less complexity.
- Code Quality vs Delivery Speed: Tools like "The Epic Stack" and AI-driven automation can help teams ship faster while maintaining stability.
- Maintainability vs Scalability: Skipping proper architecture can slow growth later. Solutions like pnpm monorepos and micro frontends provide a middle ground.
- Core Features vs UI Polish: Focus on functionality first, but ensure fast load times and reliable performance to retain users.
Major Trade-offs in Frontend Development for Startups
Frontend Framework Trade-offs: React vs Lightweight Frameworks for Startups
Choosing Between Lightweight and Feature-Rich Frameworks
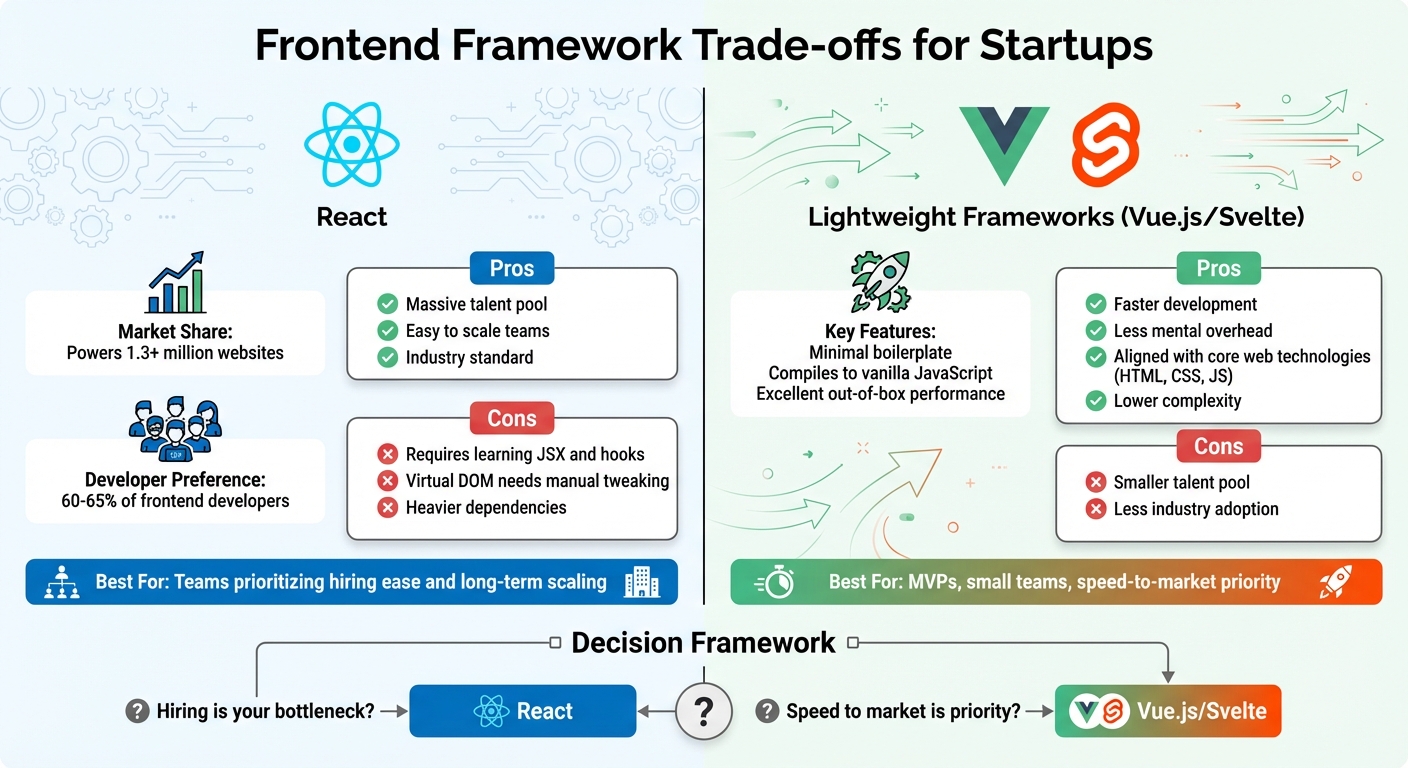
The framework you choose can shape how quickly you code, how easy it is to hire developers, and how well your app performs. React is a popular choice, powering over 1.3 million websites and backed by a massive talent pool. It’s a solid option if you need to scale your team quickly [9]. However, it comes with its quirks: React requires learning JSX and hooks, relies on a Virtual DOM that sometimes needs manual tweaking, and often includes heavier dependencies.
On the other hand, lightweight frameworks like Vue.js and Svelte take a different approach. They minimize boilerplate, compile directly to vanilla JavaScript, and deliver excellent performance right out of the gate with little need for extra tuning [9]. Developer Alicia Sykes sums it up well:
Building in Svelte makes me happy. I like that it’s both modern, intuitive and fast, but also that its SFCs are very aligned with the core web technologies: just HTML, CSS and JS [9].
For startups working on MVPs or operating with small teams, these frameworks can help you go from concept to production faster with less mental overhead [9].
Ultimately, the decision depends on your biggest bottleneck. If hiring developers is a challenge, React’s popularity makes it the safer bet. But if speed to market is your top priority, Vue.js or Svelte might be the better fit [9].
Code Quality vs Speed of Delivery
Startups constantly juggle the need to ship quickly with the importance of maintaining clean, reliable code. Tools like "The Epic Stack" simplify setup by handling testing, database configuration, and styling for you – letting you focus on building and shipping [7]. As Kent C. Dodds explains:
The trade-offs of most of the frameworks and tools you could use to build your application fit within the constraints of the vast majority of apps. Despite this, engineers consistently struggle with analysis paralysis [7].
AI tools can also speed things up, generating about 90% of a UI from a Figma mockup and automating repetitive tasks like testing in your CI/CD pipeline [6][7]. As Ajay Yadav, a front-end engineer, puts it:
AI won’t replace frontend developers; it will replace the tedious, repetitive work that hinders innovation [6].
The trick is to use AI as a starting point. Always review and refine its output before it goes into production. Pair this with automated testing from the beginning, and you can deliver quickly without sacrificing stability [7].
Maintainability vs Scalability
When speed is critical, it’s tempting to skip advanced state management or modular architecture. But this shortcut can backfire, making it harder to scale later. Tools like pnpm or Turborepo offer a middle ground, allowing you to centralize dependencies and keep your code organized across multiple packages.
For example, in January 2024, Kong’s engineering team rebuilt their "Konnect" platform using a micro frontend architecture within a pnpm monorepo. By splitting the app into domain-specific sections and using a shared "AppShell", they cut CI/CD feedback loops from 45 minutes to just 6 minutes and nearly doubled their deployment frequency. They also slashed their GitHub Actions usage from 264,000 minutes to 1,800 minutes per month [12].
The takeaway? You don’t have to choose between speed and scalability if you plan your structure wisely from the start. Keep track of technical debt and set aside time for regular refactoring to avoid future headaches [11].
UI/UX Polish vs Core Features
Startups often face a tough question: should you focus on perfecting the interface or just make it functional? The answer depends on your audience. For B2B tools, where functionality is king, a working MVP is more important than a polished prototype. Launch the core features, gather user feedback, and iterate.
That said, a functional interface still needs to be reliable. Performance matters – research shows that faster load times can increase mobile revenue per session by 17% [3]. To strike the right balance, use rapid prototyping techniques and lean on native HTML elements (like <details> for accordions) to minimize JavaScript bloat. Setting performance budgets can also help prevent regressions [8][10].
One developer managed to reduce their app’s JavaScript by 80% by shifting from a "JS-first" approach to relying more on native HTML elements. This not only improved performance but also boosted accessibility [8]. While you don’t need pixel-perfect animations on day one, you do need an interface that loads quickly and keeps users engaged.
These trade-offs highlight the balancing act startups face when building frontends. By making thoughtful decisions, you can ship fast while laying a solid foundation for future growth. The key is finding strategies that let you deliver results now without compromising long-term success.
How to Balance Speed and Long-Term Success
Build in Phases
Successful teams take an incremental approach to development, often employing the MoSCoW method to prioritize features into must-haves, should-haves, could-haves, and won’t-haves [17]. This structured approach ensures your Minimum Viable Product (MVP) remains focused and avoids "feature bloat" before launch.
Start with the "Golden Path" – a single user story that delivers the core value of your product [18]. For instance, if you’re creating a SaaS dashboard, prioritize one essential workflow, like onboarding a new user, and perfect it. Leave more complex features, such as admin panels, analytics, or integrations, for later. Edge cases and advanced user roles can also wait until the core experience has been tested and validated by real users.
When you’re ready to expand, consider using a "strangler fig" approach to add features incrementally [1]. This strategy focuses on building modularly, isolating high-impact areas like checkout processes or user profiles. By doing this, you can grow your product without overhauling the entire codebase. For example, in 2021, Mobile Twitter used this method to optimize its internationalization pipeline, implementing lazy-loading for translation strings. This reduced JavaScript execution time during the initial load by an impressive 80% [16].
Once you’ve outlined a phased plan, the next step is selecting the right tools to maintain both speed and quality.
Use Tested Frameworks and Tools
After defining your build phases, it’s time to choose frameworks and tools that align with your goals. Vue.js and Nuxt.js are excellent options for startups looking to move quickly. These frameworks offer a straightforward learning curve, built-in server-side rendering (SSR), and a streamlined developer experience [15]. As frontend architect Sudhir Mangla aptly notes:
The 2025 question isn’t ‘Which is best?’ but ‘Which fits our system’s shape, our hiring pool, and our tolerance for change?’ [15]
Automation is another critical investment from the start. Implement CI/CD pipelines to run automated tests for every code change, and use tools like Turborepo or pnpm to manage dependencies across multiple projects in a single repository [2]. This setup not only ensures consistency but also helps catch potential issues early in the development process. For pages where performance is key, leverage server-side rendering (SSR) or static site generation (SSG) to deliver pre-rendered HTML. This reduces client-side JavaScript execution, resulting in faster load times [13][14].
Consider AlterSquare‘s 90-Day MVP Program
If you’re a non-technical founder or need additional resources, AlterSquare’s 90-day MVP program can help you bridge the gap between rapid development and long-term scalability. This program offers a structured path from concept to launch, including rapid prototyping, tech stack consultation, and post-launch support. It’s designed to help you deliver a market-ready product quickly while ensuring it’s built to scale.
AlterSquare employs modern tools such as Vue.js, Nuxt.js, GoLang, and Node.js and integrates AI-driven development to streamline repetitive tasks like testing and boilerplate setup. Their process – spanning discovery, design, agile development, launch, and post-launch support – allows startups to focus on validating their business model while a dedicated team handles the technical complexities. Pricing starts at $10,000, making it an appealing option for early-stage startups looking to ship fast without compromising scalability.
sbb-itb-51b9a02
Conclusion: Making Smart Trade-offs in Frontend Development
Key Takeaways
Delivering frontend features faster requires carefully weighing trade-offs that align with your startup’s current stage and long-term goals. React remains a dominant choice in the hiring market, with 60–65% of frontend developers favoring it [15]. However, ignoring technical debt can act as a hidden "tax", dragging down daily productivity [19]. When it comes to architecture, options like SSR (server-side rendering) and SSG (static site generation) can improve initial load times but add server-side complexity. On the other hand, SPAs (single-page applications) offer quicker in-app transitions but may slow down content delivery [13].
Highly effective teams make technical debt visible by tracking metrics like "Errors Per Million" (EPM) through dashboards. This approach directly links reducing debt to improving productivity. For example, in 2019, Franco’s team at Atlassian cut Trello’s sync error rate by 75% by implementing EPM tracking and setting clear performance thresholds [19]. Additionally, fast-loading mobile experiences can drive revenue, with studies showing a potential 17% increase [3]. While some UI/UX refinements can be delayed, meeting critical performance benchmarks – like maintaining a Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) under 2.5 seconds – should be a top priority from the beginning [4].
These strategies lay the groundwork for sustainable and efficient frontend development.
Final Thoughts on Building Frontends That Last
The trade-offs and tools you choose today will shape the long-term stability and scalability of your product. Framework decisions, in particular, have a compounding effect over time [1][5]. Investing in methodologies like Feature-Sliced Design or leveraging differential serving to optimize for modern browsers may require more effort upfront, but these choices pay off in the long run. By using metrics to guide decisions, you can align your technical approach with your broader strategic goals. Instead of fixating on which framework is objectively "best", the focus should shift to selecting one that fits your system’s architecture, team expertise, and ability to adapt.
For founders without a technical background or those needing extra engineering support, working with experienced teams can simplify these decisions. AlterSquare, for instance, offers a 90-day MVP program starting at $10,000. Their process combines tools like Vue.js, Nuxt.js, and AI-driven development to quickly move from concept to launch. The ultimate goal is to ship fast, gather real user feedback, and avoid costly rebuilds later.
FAQs
What are the pros and cons of using lightweight frameworks like Vue.js or Svelte for startups?
Lightweight frameworks like Vue.js and Svelte are great options for startups looking to quickly develop and deploy fast, responsive frontends. Vue.js stands out for its impressive page load and update performance, often requiring minimal fine-tuning. On the other hand, Svelte takes a unique approach by compiling components directly into plain JavaScript, which eliminates the need for a runtime and helps shrink bundle sizes. These features can translate into smoother user experiences, quicker launches, and even reduced hosting costs – key factors for startups aiming to move fast.
That said, there are some trade-offs to weigh. While Vue’s ecosystem is solid, it’s not as extensive as React’s, which might mean fewer niche libraries or enterprise-level tools to draw from. Svelte’s compile-time approach, while efficient, can present a steeper learning curve. Its ecosystem is also less mature, with fewer third-party components and limited long-term documentation. Both frameworks require careful planning to scale effectively for larger projects, and without a focus on best practices, there’s a risk of accumulating technical debt.
For startups focused on speed, simplicity, and keeping bundle sizes small, Vue.js and Svelte are strong contenders. However, if your project demands access to a broader ecosystem or specialized tools, these frameworks might present some challenges.
How can AI tools help engineering teams build faster and better frontends?
AI tools have the potential to transform frontend development by speeding up workflows and improving code quality. They excel at automating repetitive tasks, such as generating boilerplate components, translating design mockups into frameworks like React or Vue, and even suggesting utility classes for frameworks like Tailwind – all in just seconds. This allows developers to invest more time in refining user experience and optimizing performance instead of getting bogged down in manual coding.
Beyond code generation, AI can also simplify quality assurance. It can identify layout inconsistencies, accessibility issues, and performance bottlenecks as developers build. Some tools even go a step further by automatically creating unit and integration tests, enabling teams to maintain high-quality standards even under tight deadlines. By embedding AI into workflows – whether in IDEs, CI pipelines, or design handoff processes – startups can roll out features faster while keeping their codebases scalable and easy to maintain as they grow.
How can startups ensure their frontend is both scalable and easy to maintain?
Startups can build a frontend that grows effortlessly and stays manageable by embracing a few key strategies. One of the most effective methods is focusing on modular design – breaking the code into self-contained, domain-specific components. This makes it a breeze to test, update, or add new features without causing headaches across the entire codebase.
Another important step is setting up clear coding standards and thorough documentation. This not only keeps the code consistent but also makes it much easier for new developers to hit the ground running. Pair this with tools like automated testing and continuous integration to catch problems early and maintain high-quality code as the product evolves.
Don’t forget to tackle technical debt regularly. Cleaning up unused code, fine-tuning dependencies, and keeping performance sharp ensures that your foundation stays strong as you scale. By following these practices, startups can deliver features faster while staying prepared for future growth.









Leave a Reply