AI pipelines are a game-changer for scaling products. They automate repetitive tasks, optimize resources, and keep machine learning models accurate as data grows. For startups, this means handling more users and data efficiently while controlling costs. Key benefits include:
- Automation: AI pipelines handle data ingestion, model training, validation, and deployment automatically.
- Cost Efficiency: Cloud-based pipelines use resources only when needed, reducing expenses.
- Performance: Continuous monitoring ensures models stay reliable, even as data patterns shift.
Startups can use tools like TensorFlow Extended (TFX) and MLflow to streamline workflows, enabling faster experimentation and production readiness. This approach ensures scalability and reliability, helping teams focus on innovation instead of maintenance.
Intro to AI Pipelines: Build Reliable ML Workflows
sbb-itb-51b9a02
How AI Pipelines Improve Product Scalability
AI pipelines address common startup challenges by streamlining operations in three key ways: automating repetitive tasks, optimizing resources, and enabling systems to adapt to shifting demands. These benefits become more pronounced as your product scales, helping you avoid operational bottlenecks and inefficiencies.
Automation and Efficiency
As data volumes grow, manual processes quickly become impractical. AI pipelines automate the entire workflow – from ingesting raw data to deploying models – with Continuous Training ensuring models stay up-to-date as new data comes in [1][3][5]. Tools like Vertex AI Pipelines and Apache Airflow orchestrate these workflows, automatically advancing tasks based on predefined conditions [1][8].
"Automation minimizes human error, helping ensure models are trained on high-quality data and consistently optimized for performance." – Snowflake [5]
When rolling out updates, startups can rely on canary releases, which initially serve only 10% to 20% of live traffic to the new model version. This approach validates performance before a full deployment [1]. Modular pipeline components can also be reused across different projects, making testing simpler and increasing overall reliability [8]. This automation not only speeds up execution but also sets the stage for saving costs and improving performance.
Cost Optimization and Resource Allocation
Scaling your product doesn’t have to mean runaway expenses. Cloud-native AI pipelines separate storage from compute resources, so you only pay for what you actually use [5]. Features like autoscaling dynamically adjust resources based on real-time demand – whether it’s increasing CPU power during training or handling spikes in inference requests [9].
"A primary benefit of adopting MLOps practices is a reduction in costs for technology and personnel. Automation helps you avoid the duplication of ML activities and reduce the workload for data scientists and ML engineers." – Google Cloud Architecture Framework [9]
AI pipelines also use smart scheduling, retraining models only when necessary instead of following fixed cycles. Managed services like Vertex AI or Cloud Run allow systems to scale down to zero during idle periods, eliminating unnecessary costs [9][2]. Additionally, tagging resources by project or model name provides clear visibility into spending, helping teams manage budgets more effectively [9].
Better Performance and Agility
When user demand spikes, speed is everything. AI pipelines enable parallel execution, letting multiple tasks – like infrastructure checks and model evaluations – run at the same time. This significantly shortens deployment times [1]. For applications like fraud detection or dynamic pricing, real-time pipelines process data as it’s generated, ensuring immediate responses [11].
Using Docker containers ensures consistent performance, whether serving 100 or 100,000 users [1]. Automated drift detection alerts teams to model degradation, allowing fixes before accuracy issues affect users [11]. And because modern pipelines are modular, you can update specific components without having to rebuild the entire system, giving you the flexibility to adapt as your product evolves [12].
| Scaling Method | Approach | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Horizontal Scaling | Adding more machines (scaling out) | Fault tolerance and large-scale workloads [12] |
| Vertical Scaling | Upgrading existing hardware (scaling up) | Lower latency for single-threaded tasks [12] |
| Batch Pipelines | Processing data at intervals | Training models on historical datasets [11] |
| Real-Time Pipelines | Processing data as it’s generated | Immediate inference for tasks like fraud detection [11] |
These strategies not only improve efficiency but also prepare your AI pipelines for long-term scalability and adaptability.
Building Blocks of Scalable AI Pipelines
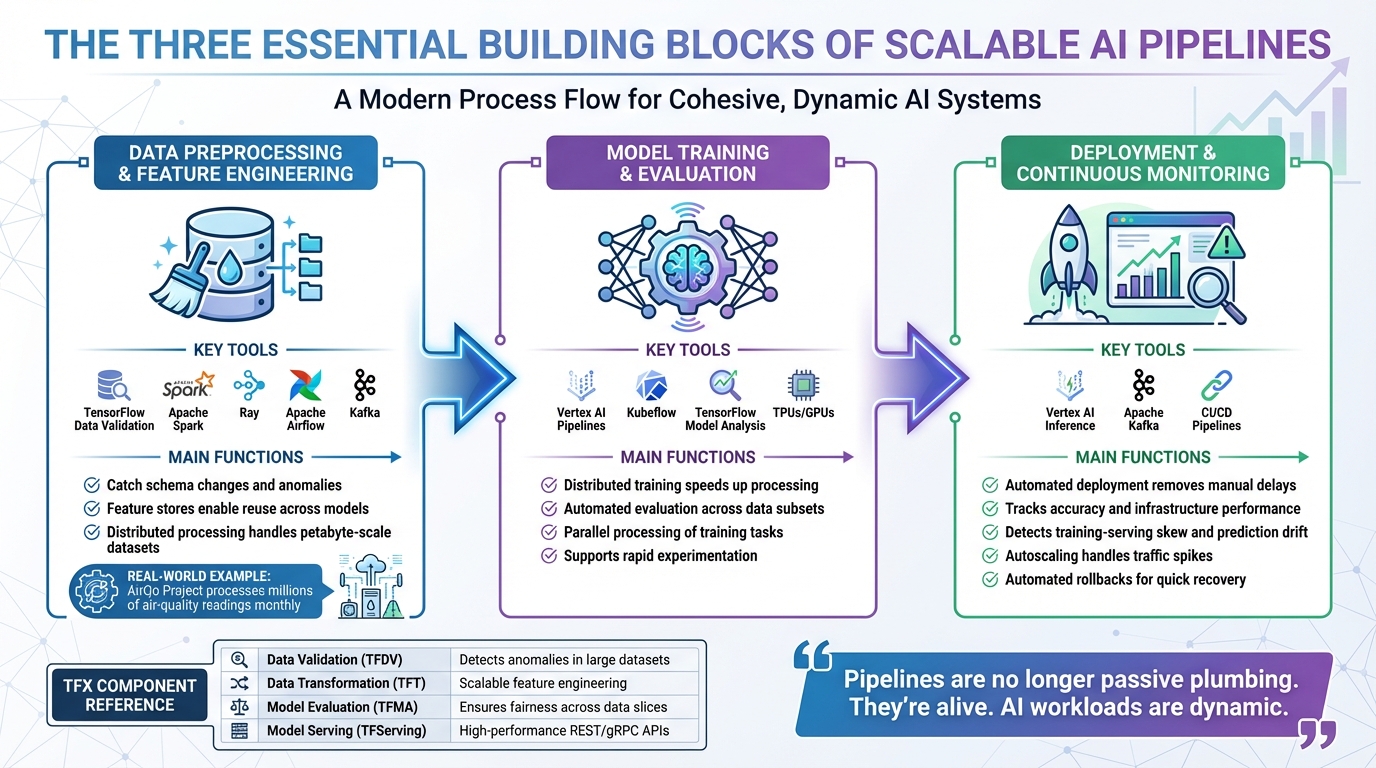
Three Building Blocks of Scalable AI Pipelines: Data Preprocessing, Model Training, and Deployment
After achieving automation and efficiency, these core components ensure AI pipelines can handle increasing data and user demands over time. Scalable AI pipelines rely on three essential pillars to maintain performance and adaptability.
Data Preprocessing and Feature Engineering
Clean, reliable data is the backbone of scalable AI systems. Tools like TensorFlow Data Validation help catch schema changes and anomalies early, preventing errors that could derail model training [6][1]. Without high-quality data, even the best algorithms will produce flawed results [13].
Feature stores play a key role by enabling the reuse and sharing of complex, computationally expensive features across multiple models [13][4]. A great example is the AirQo Project in Africa, which processes millions of air-quality readings monthly. Using Apache Airflow and Kafka for real-time processing, they built a pipeline that could scale across the continent while remaining dependable under heavy loads [15].
"Pipelines are no longer passive plumbing. They’re alive. AI workloads are dynamic. Enrich. Label. Contextualize. Repeat. Or die." – Lee James, Senior Partner, Domo [15]
To handle large-scale operations, modularity is crucial. It allows pipelines to adapt quickly to new data sources [13]. By distributing preprocessing tasks across clusters with tools like Apache Spark or Ray, systems can process massive datasets – up to petabytes – without running into bottlenecks [16]. This step sets the stage for efficient model training and evaluation.
Model Training and Evaluation
As datasets grow, training workflows must be equipped to manage them efficiently. Distributed training on hardware like TPUs or GPUs significantly speeds up this process, making it possible to handle enormous datasets [4][1]. Tools like Vertex AI Pipelines or Kubeflow automate the execution of training and validation tasks, ensuring smooth parallel processing [1][14].
Automated evaluation tools such as TensorFlow Model Analysis help maintain model quality by assessing performance across various data subsets, like demographics or locations. This ensures that models perform consistently across a diverse user base [6]. Without this, a model might excel overall but fail for certain user groups.
"Investing in the automation of the machine-learning pipeline eases model updates and facilitates experimentation." – Machine Learning in Production: From Models to Products [13]
Distributed training not only accelerates updates but also supports rapid experimentation. This flexibility allows teams to test new ideas without overhauling the entire pipeline, making it easier to adapt models to evolving needs.
Deployment and Continuous Monitoring
Automated deployment and monitoring ensure models remain accurate and reliable over time. CI/CD pipelines streamline the frequent deployment of new model versions, removing manual delays [1][6].
Continuous monitoring is vital for tracking both model accuracy and infrastructure performance. It identifies issues like training-serving skew (when production data differs from training data) and prediction drift (when real-world patterns change), automatically triggering retraining when necessary [6][1]. Tools like Vertex AI Inference use managed prediction nodes and autoscaling to handle traffic spikes without compromising responsiveness [4][1].
Resilient systems often rely on event-driven architectures with message queues like Apache Kafka. These architectures decouple pipeline components, allowing different parts to scale or recover independently [8]. Automated rollbacks add another layer of security, enabling quick reversion to stable model versions if performance issues arise [4].
| Pipeline Component | TFX Library | Scalability Contribution |
|---|---|---|
| Data Validation | TFDV | Detects anomalies and schema skews in large, evolving datasets [6] |
| Data Transformation | TFT | Performs scalable feature engineering and embeds it into the exported model [6] |
| Model Evaluation | TFMA | Evaluates performance across data slices to ensure fairness and quality at scale [6] |
| Model Serving | TFServing | Deploys models as high-performance REST/gRPC APIs for online inference [6] |
Together, these components form a cohesive system that can grow alongside your product. By automating and modularizing each step, you eliminate manual bottlenecks, paving the way for smooth scalability.
Using TFX and MLflow for Scalable AI Pipelines
When building scalable AI pipelines, choosing the right tools is crucial for streamlining workflows and managing growth. Two powerful frameworks – TensorFlow Extended (TFX) and MLflow – offer distinct benefits, addressing different stages of the machine learning lifecycle. Together, they provide startups with the tools to scale effectively.
TensorFlow Extended (TFX) for End-to-End Pipelines
TFX is a robust, end-to-end platform designed to handle every step of the machine learning pipeline [17]. It organizes key components – like data validation, preprocessing, model evaluation, and serving – into a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) optimized for high-performance tasks [20]. By automating processes such as anomaly detection, data preprocessing, and model evaluation, TFX tackles common production challenges. For deployment, TensorFlow Serving converts trained models into APIs (REST or gRPC) capable of handling large-scale inference workloads [6].
"TFX is an end-to-end platform for deploying production ML pipelines." – TensorFlow [17]
A real-world example of TFX in action is Google Play, which adopted it in 2017 to refresh its machine learning models continuously. This resulted in a 2% increase in app installs while reducing custom code and speeding up experiment cycles [21]. Other major players like Spotify, Airbus, and Gmail also rely on TFX to manage their large-scale machine learning operations.
TFX supports various orchestrators, including Apache Airflow, Apache Beam, and Kubeflow Pipelines, offering flexibility in deployment. It also integrates seamlessly with managed services like Google Cloud Dataflow and Vertex AI, making it easier to scale compute-intensive tasks. Additionally, it supports TensorFlow Lite for efficient on-device inference [17]. While TFX shines in production-grade pipelines, MLflow complements it by focusing on experimentation and lifecycle management.
MLflow for Experimentation and Deployment Management
Where TFX excels at production pipelines, MLflow is all about speeding up experimentation [18]. It automatically tracks experiments, ensuring version control, reproducibility, and auditability. Its centralized model registry acts as a single source of truth, simplifying deployment management.
"MLOps transforms machine learning into a robust engineering discipline." – Hashone Global [18]
MLflow’s modular design allows teams to break down pipelines into reusable components for tasks like data preprocessing, feature engineering, and model training. These components can be managed and scaled independently. When paired with Docker and Kubernetes, MLflow ensures consistent model behavior across development, testing, and production environments [18]. It can even trigger automatic retraining when performance drops below a certain threshold or when significant data drift is detected [19]. For startups, the ideal workflow starts with MLflow for quick experimentation, transitioning to TFX for full-scale production systems once models prove successful.
How AlterSquare Integrates These Tools
AlterSquare combines TFX and MLflow within its I.D.E.A.L. Framework to deliver scalable AI solutions tailored to client needs. During the Discovery & Strategy phase, the team evaluates whether a product requires TFX’s full production capabilities or if MLflow’s lighter experimentation tools are sufficient. Factors like dataset size, growth projections, and the need for consistent training and serving are considered [20].
For early-stage startups, AlterSquare often begins with MLflow to enable rapid experimentation and iteration. As the product matures and data volumes grow, TFX components are gradually introduced. This starts with data validation and transformation, eventually incorporating automated evaluation and serving as demand increases.
Through its AI-Driven Solutions, AlterSquare configures TFX pipelines using YAML, integrating them with clients’ existing CI/CD systems. This approach reduces technical debt, eliminates manual errors, and aligns with CI/CD best practices [6]. By orchestrating workflows with tools like Vertex AI Pipelines or Apache Airflow, AlterSquare ensures consistency across environments. For clients focused on Application Modernization, the use of ML Metadata enhances reproducibility and auditability, making pipelines easier for new team members to understand and maintain.
Challenges and Solutions in Adopting AI Pipelines
Integration with Existing Systems
As companies scale their AI efforts, integrating pipelines into existing systems becomes increasingly complex. Startups, in particular, often struggle with the "handoff" gap between data scientists focused on experimentation and engineers responsible for production. This disconnect can lead to training-serving skew, where the features used during model training differ from those in production. The result? Models that perform well in testing but fail to deliver in real-world scenarios.
A modular architecture can bridge this gap. Using containerization tools like Docker allows teams to decouple the environment from the code, ensuring consistent performance across development and production. Additionally, a feature store provides a centralized repository for feature definitions, ensuring that both data scientists and engineers work with the same data. These solutions not only eliminate training-serving skew but also create a smoother path for tackling other challenges, such as technical debt and skill shortages.
Technical Debt and Skills Gaps
"80% of AI development time is spent on data preparation." – Andrew Ng, Founder, DeepLearning.AI [23]
AI systems accumulate technical debt at a much faster rate than traditional software. This is largely due to the intricate infrastructure required for tasks like data verification, configuration, and monitoring [22]. Many startups find themselves bogged down by poorly structured code, where experimental notebook scripts can’t easily transition into production-grade systems.
Managed services like Vertex AI can ease this burden by offering serverless orchestration, reducing the need for deep infrastructure expertise [2]. Instead of building everything from scratch, teams can rely on predefined components for common tasks like data preprocessing. Implementing continuous training (CT) pipelines ensures that models are automatically retrained with fresh data, minimizing the manual workload for small teams. To maintain reproducibility and streamline onboarding for new team members, leverage metadata stores to track every artifact’s lineage [2][7]. These practices not only address technical debt but also lay a strong foundation for compliance and governance.
Compliance and Data Governance
As AI systems scale, compliance and data governance become increasingly critical. Alarmingly, only 38% of organizations actively address compliance risks in their AI workflows, even though 63% acknowledge these risks [24]. Poor data quality alone costs organizations an average of $12.9 million annually [24]. With regulations like GDPR and the EU AI Act, ensuring compliance is no longer optional – it’s a necessity.
Start with comprehensive data lineage tracking to create a transparent audit trail. This ensures that every data source and transformation is documented, making regulatory investigations smoother. Incorporate automated data quality checks throughout your pipeline to catch issues early and prevent "data cascades", where poor-quality data amplifies downstream problems [8][23]. Protect sensitive information using role-based access control (RBAC) and encryption. Before deploying new models, use shadow testing to validate performance without impacting users [23]. These measures not only help with compliance but also build trust in your AI systems.
AlterSquare’s Approach to Implementing AI Pipelines
Phased Integration Using the I.D.E.A.L. Framework
Taking an AI demo and turning it into a production-ready pipeline isn’t easy. Demos often perform well because they rely on clean data and controlled environments. But in production, the landscape changes – messy inputs, traffic surges, and unexpected API failures are just a few of the hurdles [25]. AlterSquare tackles these challenges with its I.D.E.A.L. framework, which breaks the process into five clear steps: discovery and strategy, design and validation, agile development, launch preparation, and post-launch support.
During the discovery phase, the focus is on validation first. For example, AlterSquare uses deterministic logic to handle malformed text or unusual languages before data even reaches the model [25]. In the agile development phase, pipelines are built as modular components. This modularity allows for independent testing and updates, avoiding disruptions to the whole system [8][13]. To ensure consistency between development and production, containerization is applied, isolating the execution environment from the code [6][1]. This method has proven to be a game-changer, cutting the time to deploy machine learning solutions from months to just weeks [21].
A recent case study demonstrates how this phased approach can scale SaaS products effectively.
Case Study: Scaling a SaaS Product with AI Pipelines
AlterSquare partnered with a growth-stage startup struggling with a significant bottleneck. Their MVP had a single logical flow, resulting in 10-minute processing times and frequent crashes when multiple users accessed the system simultaneously [26]. To address this, AlterSquare restructured the system, breaking it into separate components like API, background processing, and orchestration. They moved from manual orchestration to Kubeflow-based Vertex AI Pipelines, which allowed for autonomous release management and faster delivery of results [30].
The impact was immediate. A unified semantic versioning system was introduced, ensuring traceability and reproducibility. This allowed the team to confidently track the system’s state at any given time [29]. Scaling costs were also tackled by adopting serverless inference, spot instances, and aggressive auto-scaling to shut down idle resources [28]. To keep models performing well over time, automated monitors were set up to detect shifts in input data distributions. If a shift occurred, the system would alert the team and trigger retraining [28][10]. In one instance at Google Play, these automated pipelines contributed to a 2% increase in app installs by improving data analysis and model performance [21].
Lessons Learned: Overcoming AI Integration Challenges
Real-world implementations have revealed some key takeaways.
First, ownership is critical. Misalignment between data scientists and deployment engineers can lead to system breakdowns. AlterSquare addresses this by fostering an MLOps culture where the entire pipeline is treated as a shared responsibility [28]. They also avoid using non-modular tools like Jupyter Notebooks for production, instead opting for a modular approach where tasks like data cleaning and model training are separated into testable scripts [28].
Second, edge cases matter. Rare scenarios in real-world data often cause models to fail. To counter this, AlterSquare ensures that training data includes complex variations, helping models better handle these situations [27]. Additionally, they’ve learned that while refactoring can fix localized issues, rebuilding is necessary when shortcuts from demos make their way into production [25]. By implementing Continuous Integration (CI), Continuous Delivery (CD), and Continuous Training (CT) pipelines, they ensure that updates – whether from new models or fresh data – are deployed consistently and reliably [6][1].
Conclusion: Scaling Products with AI Pipelines
Key Takeaways for Founders and Product Teams
AI pipelines have become a critical tool for startups looking to scale efficiently. By automating continuous training, these pipelines allow models to adjust to new data patterns without requiring manual updates [1][6]. One essential aspect to prioritize is reproducibility. With proper version control for code, data, and models, teams can ensure smooth transitions from research to production, confident that training conditions can always be replicated [8].
Another vital approach is adopting a modular architecture. Designing pipelines as interchangeable components simplifies testing, encourages code reuse, and makes it easier to update implementations as needed [8]. This method works seamlessly with end-to-end observability, which helps detect subtle issues like data drift or discrepancies between training and serving environments – problems that traditional monitoring tools often miss [4][8]. Companies like Spotify, Airbus, and Gmail have successfully leveraged tools like TensorFlow Extended (TFX) to handle large-scale machine learning tasks, proving these strategies are effective at any level [17].
To keep systems up-to-date, teams should implement CI/CD/CT pipelines. Tools such as Git for code, DVC for managing datasets, and MLflow for tracking models provide a comprehensive audit trail [8]. Managed services like Dataflow and Vertex AI can further streamline scaling, while feedback loops ensure retraining is triggered when anomalies arise [1][4]. Autoscaling policies also prepare systems to handle unexpected traffic surges [4].
By emphasizing automation, modular design, and continuous integration, AI pipelines create a solid foundation for scalable, reliable products. These strategies pave the way for growth, and AlterSquare is ready to assist in making them a reality.
How AlterSquare Can Help
AlterSquare offers tailored expertise to help teams implement these strategies effectively. Using its I.D.E.A.L. Framework, the firm breaks down complex implementation processes into clear, manageable steps. AlterSquare also integrates trusted tools like TensorFlow Extended and MLflow, helping startups tackle challenges such as technical debt, skill shortages, and data governance issues. With a focus on modular design and continuous learning, their approach ensures models stay accurate by retraining automatically as market conditions evolve [11][31].
Whether you’re launching your first MVP or upgrading an older system, AlterSquare’s Engineering-as-a-Service provides the knowledge and resources you need to scale successfully. From quick prototyping to ongoing support after launch, their team becomes an extension of yours – delivering reliable code, user-friendly designs, and AI-powered solutions that drive innovation.
FAQs
When should I start building an AI pipeline?
When your workflow shifts from one-off experiments to a structured, repeatable process, it’s time to start building an AI pipeline. This stage usually comes after the initial experimentation phase and focuses on clearly defining inputs and outputs, choosing the right tools, and ensuring the process is sturdy and dependable.
Creating a production-ready pipeline becomes crucial when you need to scale, automate, or maintain your project. It allows you to handle key tasks like data ingestion, preprocessing, deployment, and monitoring with efficiency, ensuring your project is prepared for long-term growth and performance.
How do I choose between TFX and MLflow?
Choosing between TFX (TensorFlow Extended) and MLflow comes down to what you need for your machine learning workflow.
TFX is a great choice if you’re building scalable, production-ready pipelines, especially for TensorFlow models. It comes with a suite of tools for tasks like data ingestion, validation, training, and deployment – all tailored for robust, end-to-end pipelines.
On the other hand, MLflow shines when it comes to experiment tracking, model packaging, and offering flexibility across multiple frameworks. It’s particularly useful if your work involves diverse tools and frameworks beyond TensorFlow.
When making your decision, think about the complexity of your pipeline, the expertise of your team, and the infrastructure you’re working with. These factors will guide you toward the best fit.
What’s the easiest way to catch model drift early?
The simplest method to spot model drift early is by adding automated drift detection into your machine learning pipeline. With self-healing pipelines, you can keep an eye on data and model performance at all times. These pipelines can detect concept drift or changes in data distribution and automatically trigger retraining when necessary.
On top of that, using observability practices – such as anomaly detection and performance monitoring – can help you catch even the smallest shifts. This ensures you can act quickly to maintain your model’s accuracy and keep your product running smoothly.









Leave a Reply